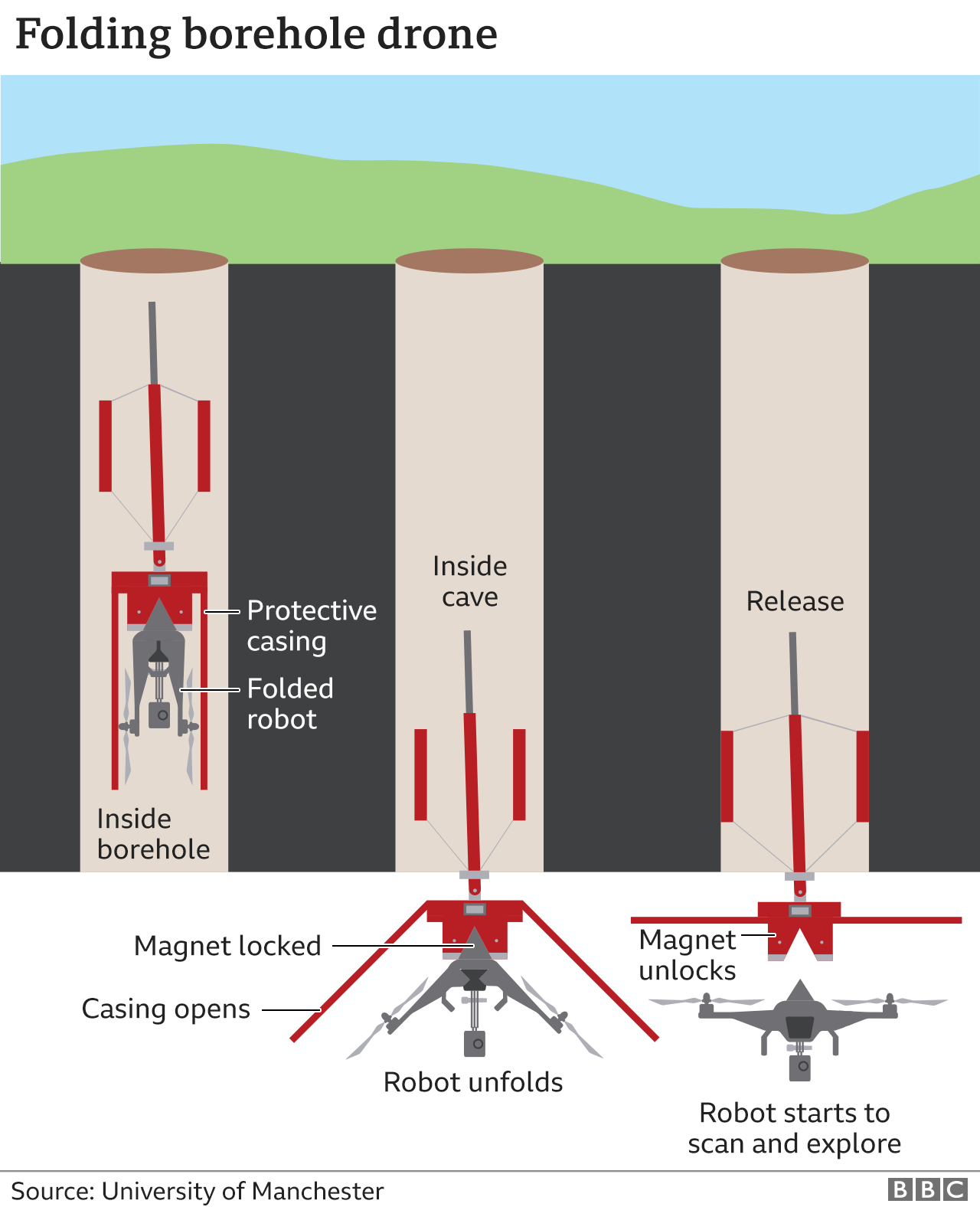
Drones have become a vital piece of kit for surveyors.
Deploying unmanned aircraft on job sites yields fast and accurate data capture – gathered safely and efficiently.
One statistic shows that collecting topographic data with a drone is up to five times faster than with land-based methods and requires less manpower.
But what is the best drone for aerial surveying and mapping?
Until recently, the two DJI drones which stood out were the Phantom 4 RTK and the M210 RTK V2 with X7 camera.
However, the unveiling of the P1 camera (below, left) and L1 LiDAR sensor (below, right) for the M300 RTK has changed things dramatically, transforming DJI’s flagship commercial drone into a powerful aerial surveying tool.
So how does the M300 RTK compare to the Phantom 4 RTK and M210 RTK with X7 camera, and what are the advantages of deploying them on your job site?
Introduction
DJI released the Phantom 4 RTK in 2018 as a dedicated, out-of-the-box, all-in-one solution for low-altitude surveying and mapping.
The DJI M210 RTK V2 is part of the DJI M200 Series V2. While it is not a dedicated surveying drone, it can be utilised for these missions when integrated with the Zenmuse X7 camera and the 24 mm/35 mm lenses (to be purchased separately).
Recently, DJI unveiled the M300 RTK, a totally revamped and next-level version of the popular Matrice Series.
The M300 RTK cannot be integrated with the X7 camera, but it can carry the new P1 and L1 sensors (purchased separately), which are dedicated to aerial mapping and surveying.
The M210 RTK V2 and the M300 RTK can also be integrated with other DJI and third-party payloads, to further expand their versatility.
Which Drone Has The Better Camera For Mapping And Surveying?

Camera quality is a major consideration when it comes to aerial surveying.
Firstly, photogrammetry missions.
Drone photogrammetry is when a drone captures a large number of high-resolution images over a specific area. These images can then be processed by specialist software to generate accurate and realistic models of the world, which include key data such as measurements.
Prior to the release of the P1, the X7 was DJI’s premier solution, with its 24MP camera, and choice of 24 mm and 35 mm lenses.
Other lense options are available for the X7, but the 24 mm and 35 mm (pictured) are opitmised for surveying and can store imagery with geotagged centimetre-level precision.
However, the P1 has changed things significantly, thanks to its 45MP full-frame low-noise high-sensitivity sensor.
Ultimately, better resolution equals better accuracy and, eventually, more precise 3D models.
P1 operators also have the choice of three interchangeable lenses: 24 mm, 35 mm, and 50 mm.
This gives greater versatility. A 35 mm lens is suitable for most mapping scenarios, but if the UAV operation needs to be higher, the 50 mm lens can be used. Similarly, the 24 mm is available for lower altitude flights.
In contrast, the Phantom 4 RTK has a fixed camera/lens which can capture 20MP imagery, with a focal length of 8.8 mm.
Having interchangeable lens options not only expands versatility, but it can also help to improve ground sample distance, which in turn boosts mission efficiency.
This is especially helpful for flying in a city environment and near to high-rise buildings – improving the operating radius and safety in the process.
Safety Features
Safety is an important part of any drone flight and the DJI ecosystem is among the safety on the market.
M300 RTK
As DJI’s flagship commercial drone, the M300 RTK sets a new standard for safety, and is the company’s safest platform yet.
These enhanced safety features include six direction dual visual sensors, dual Time-of-Flight (TOF) sensors, dual auxiliary lights, and an adjustable detection range of between 1 to 40m.
The aircraft also benefits from DJI’s AirSense technology – which enhances airspace safety by automatically providing the operator with real-time information about nearby airplanes and helicopters.

Meanwhile, advanced redundancy features include the three-propeller Emergency Landing, and Dual Operator Control.
To further increase flight safety, the M300 RTK has a maximum wind speed resistance of 15 m/s and an IP45 rating.
While this isn’t a complete waterproofing, DJI has stated that the M300 RTK can withstand 100 mm of rain during a 24-hour period.
This robustness ensures that missions can be conducted in tricky conditions – reducing downtime.
If you need to perform operations in extreme weather conditions, the Matrice 300 RTK could be the best surveying drone for you.
Find out how water-resistant the M300 RTK is by clicking here.
M210 RTK V2
By comparison, while the M210 RTK V2 doesn’t include as advanced safety features as the M300 RTK, it is still a very reliable drone.
It has DJI’s AirSense technology, top and bottom anti-collision beacons, and front, bottom and upper obstacle avoidance sensors.
The M210 RTK V2 has an IP43 rating, which means that the drone can operate in light rain, and a wind-speed resistance of 12 m/s. You can read our guide to flying in the rain, here.
The M210 RTK V2 also has dual RTK antennas, providing powerful antimagnetic interference capability and holding the drone steady – a crucial factor if operating close to infrastructure.
Phantom 4 RTK
The Phantom 4 RTK does not benefit from such an array of safety features, nor does it have an IP rating, but it is still a reliable option.
The drone benefits from OcuSync technology, and has an obstacle sensing range of 0.7 metres to 30 metres.
Thanks to RTK, the drone can automatically resume a mission after the battery has been replaced.
The Phantom 4 RTK benefits from OcuSync technology.
DJI M300 RTK v M210 RTK V2 v Phantom 4 RTK – Which Is The Best Surveying Drone?
Drones have become a vital tool for surveying and the M300 RTK, M210 RTK V2 and Phantom 4 RTK are very capable platforms for the job.

The Phantom 4 RTK is a dedicated surveying drone, so if that is your only requirement, it is a suitable option.
The Phantom 4 RTK is a purpose-built surveying drone. It’s out-of-the-box capabilities ensure a quick launch and its user-friendly design and controls make it an ideal companion for surveyors who are starting out with drones on their job site.
The Phantom 4 RTK is especially suited for low-altitude mapping missions, over smaller job sites.
Meanwhile, the M210 RTK V2 offers greater versatility – able to carry a range of payloads for different types of missions – while the X7 camera does provide that extra bit of quality over the Phantom 4 RTK’s sensor.
Are There Any Other Options?
While the M300 RTK, Phantom 4 RTK and M210 RTK V2 are some of the best surveying drones within the DJI ecosystem, there are other options from the world’s leading drone-maker.
The M600 Pro is a robust heavy-lift surveying solution which benefits from the Lightbridge 2 HD transmission system.

Integrate the drone with a high-resolution third-party payload, like the 42MP Sony RX1R II sensor, to make it a comprehensive surveying and mapping platform.
It can also carry quality sensors such as the Z30 and XT2 for added mission versatility.
World-renowned engineering and design company Atkins used Heliguy’s research and development team to integrate the Sony RX1R II sensor with the DJI M600 Pro.
This provided a tailored solution to meet the business’s specific survey requirements.
Atkins was able to create 3D models like this.

Phantom 4 Multispectral
If agriculture is your specialty, then the high-precision Phantom 4 Multispectral is the best surveying drone for you.

The drone is capable of gathering precise plant-level data.
It also collects data with one RGB camera and a multispectral camera covering Blue, Green, Red, Red Edge, and Near Infrared bands – all at 2MP with global shutter, on a 3-axis stabilised gimbal.
Written by Heliguy | 10 Dec 2020

:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/68652449/bandicam_2021_01_11_17_16_20_402.0.jpg)
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22228821/bandicam_2021_01_11_17_16_20_990.jpg)